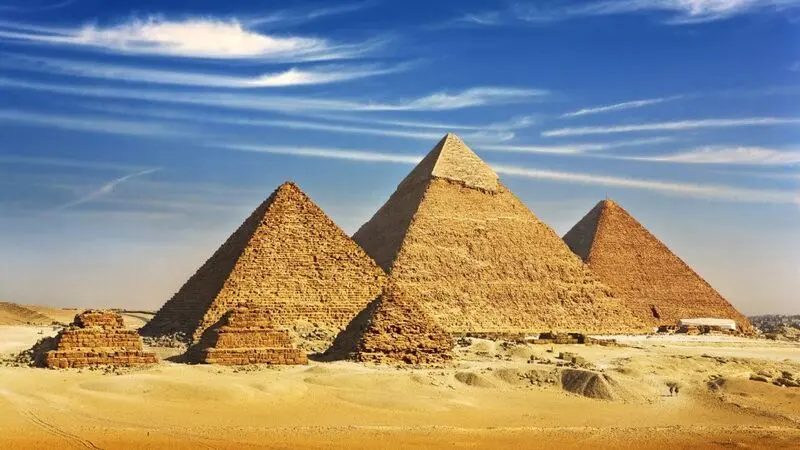
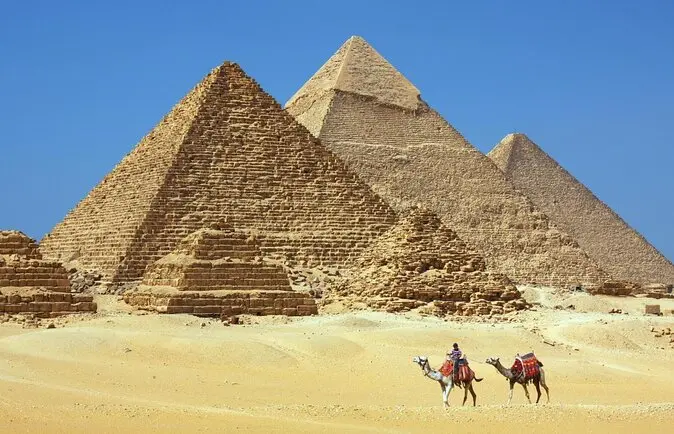
The Pyramid of Giza, also known as the Great Pyramid, is one of the most iconic structures in the world. Located in Giza, Egypt, the pyramid was built more than 4,500 years ago and is considered one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
Here is a detailed overview of the Pyramid of Giza
History of Pyramid Of Giza:
The Pyramid of Giza was built during the reign of Pharaoh Khufu, who ruled during the Fourth Dynasty of Ancient Egypt. The construction of the pyramid began around 2580 BC and was completed over a period of 20 years. The pyramid was built as a tomb for Pharaoh Khufu and was originally covered in white limestone, which has since been removed.

Construction:
The Pyramid of Giza was constructed using approximately 2.3 million limestone blocks, each weighing between 2 and 80 tons. The blocks were quarried locally and transported to the site using a system of ramps and sledges. The pyramid stands at a height of 147 meters and has a base of 230 meters, making it the largest of the three pyramids in Giza.
Interior:
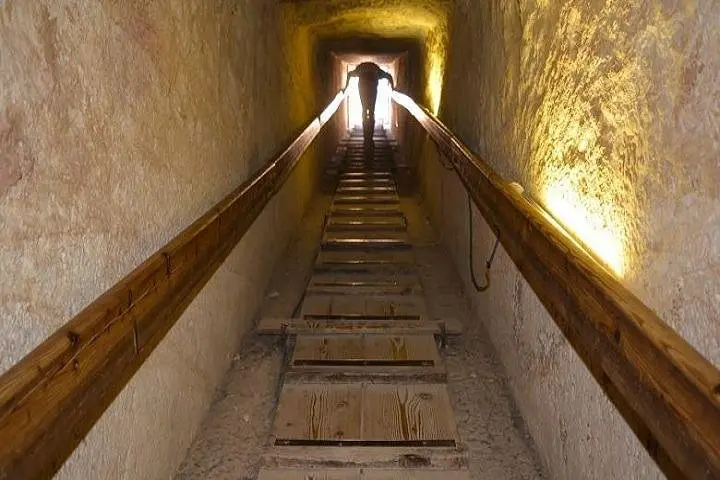
The interior of the pyramid is made up of a series of corridors and chambers. The entrance to the pyramid is located on the north face and leads to a descending passage that is 1.2 meters wide and 1 meter high. This passage leads to a subterranean chamber, which was intended to be the original burial chamber but was never used. A series of ascending passages lead to the Grand Gallery, a corridor that is 47 meters long and 8 meters high. The Grand Gallery leads to the King’s Chamber, which is the final resting place of Pharaoh Khufu. The chamber is made of red granite and measures 5.8 meters long, 10.5 meters wide, and 5.2 meters high. The chamber also contains an empty sarcophagus, as the pharaoh’s remains were likely moved to another location.

Construction Techniques:
The construction techniques used to build the pyramid are still not completely understood, and much of the process remains a mystery. However, it is believed that the workers used copper chisels and stone hammers to shape the blocks. They were then transported to the site using sledges and rollers. The blocks were then lifted into place using a system of ramps and pulleys.
Significance:
The Pyramid of Giza is one of the most significant structures in the history of Ancient Egypt. It is a testament to the incredible engineering and architectural skills of the civilization. The pyramid also played a significant role in Ancient Egyptian religion. It was believed to be the gateway to the afterlife. The pyramid was also a symbol of the pharaoh’s power and authority and was intended to protect the pharaoh’s body in the afterlife.

Tourism:
Today, the Pyramid of Giza is one of the most popular tourist destinations in Egypt, and millions of visitors come to see the it every year. Visitors can enter the pyramid and explore its interior, although the number of visitors is limited to preserve the structure. The pyramid is also surrounded by other ancient sites, including the Sphinx and the Pyramid of Khafre.
Challenges:
Despite its iconic status, the Pyramid of Giza faces several challenges in terms of preservation and maintenance. The structure is vulnerable to erosion and weathering, and many of the limestone blocks have become damaged over time. In addition, the pyramid is at risk from pollution and the effects of tourism. The Egyptian government has taken steps to preserve the pyramid, including limiting the number of visitors and implementing conservation programs.
In conclusion, the Pyramid of Giza is an incredible feat of engineering and architecture that has captured the imagination of people for thousands of years.