The timing of meals plays a significant role in our overall health and well-being. Among the various mealtime practices, the concept of an early dinner has gained attention for its potential health benefits. An early dinner refers to consuming the evening meal at an earlier hour, typically a few hours before bedtime. By understanding the advantages of an early dinner, you can make informed choices about your eating habits and optimize your well-being.
This article explores the benefits of adopting an early dinner routine, focusing on its impact on digestion, sleep quality, weight management, and overall health
Improved Digestion and Metabolism with early dinner
1.1. Enhancing Digestive Efficiency:
Eating an early dinner allows for ample time for digestion before bedtime. The body’s natural circadian rhythms align with the digestive process, and giving your digestive system sufficient time to work efficiently can result in better nutrient absorption and minimized digestive discomfort.

1.2. Reduced Acid Reflux and Heartburn:
Having dinner earlier in the evening can reduce the likelihood of experiencing acid reflux and heartburn. By allowing more time for digestion, you minimize the risk of stomach acid flowing back into the esophagus while lying down, a common trigger for these symptoms.
1.3. Balancing Blood Sugar Levels:
Having dinner earlier can help regulate blood sugar levels. Eating closer to bedtime can lead to elevated blood sugar levels, as the body’s insulin sensitivity tends to decrease later in the day. Consuming an early dinner allows the body to utilize glucose more effectively and prevent blood sugar spikes.
Enhanced Sleep Quality with early dinner
2.1. Promoting Restful Sleep:
A significant benefit of an early dinner is its positive impact on sleep quality. Eating closer to bedtime can disrupt sleep by stimulating digestion, increasing body temperature, and causing discomfort. By allowing for a few hours between dinner and bedtime, the body has time to process food and enter a more relaxed state, leading to deeper and more restorative sleep.
2.2. Reducing Nighttime Bathroom Trips:
Late-night meals can increase the likelihood of nocturia (frequent nighttime urination), disrupting sleep patterns. By consuming dinner early, you can reduce the volume of urine produced before bedtime, promoting uninterrupted sleep.

Weight Management
3.1. Regulating Caloric Intake:
Having an early dinner can aid in weight management by regulating caloric intake. Eating closer to bedtime may lead to overeating, as the body’s energy requirements decrease in the evening. By consuming dinner earlier, you align your mealtime with your body’s natural metabolic rhythms, reducing the likelihood of excessive calorie consumption.
3.2. Facilitating Intermittent Fasting:
Adopting an earlier dinner routine can also support intermittent fasting, a popular eating pattern associated with weight management and various health benefits. By allowing a longer overnight fasting period, an early dinner can extend the fasting window, promoting fat burning and enhancing metabolic flexibility.

Improved Nutrient Absorption with early dinner
1. Optimal Nutrient Utilization:
The body’s ability to absorb and utilize nutrients is influenced by the timing of meals. Consuming an early dinner ensures that the body has ample time to absorb essential vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients before bedtime. This promotes optimal nutrient utilization and supports overall health and well-being.

Regulation of Hormonal Balance
5.1. Balancing Ghrelin and Leptin Levels:
An early dinner can positively impact hormone regulation. Ghrelin, the hunger hormone, decreases after a meal, while leptin, the satiety hormone, increases. Eating earlier in the evening allows these hormones to regulate properly, reducing late-night cravings and promoting healthier food choices.
5.2. Maintaining Circadian Rhythms:
The timing of meals affects the body’s internal circadian rhythms. An early dinner helps maintain the alignment of these rhythms, optimizing hormonal balance, metabolism, and other physiological processes. Proper regulation of circadian rhythms is crucial for overall health and vitality.

Psychological and Emotional Well-being
6.1. Stress Reduction:
Eating an early dinner can contribute to stress reduction. Consuming a satisfying meal earlier in the evening allows for relaxation and promotes a sense of well-being, reducing the rush and stress associated with late-night meal preparation.
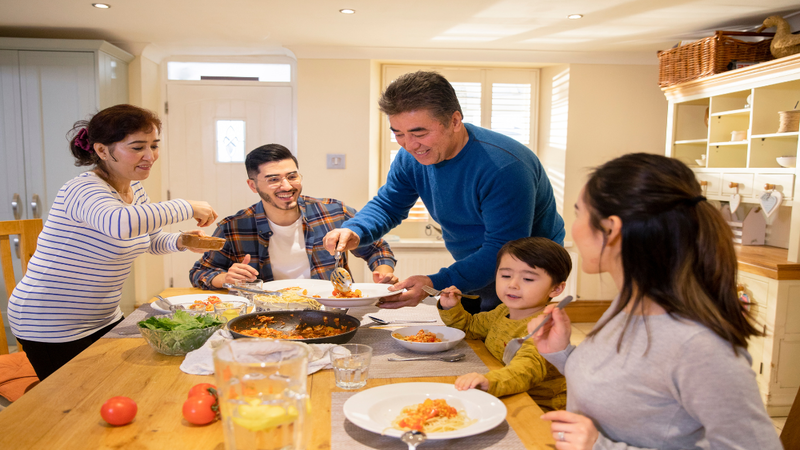
6.2. Enhancing Family and Social Connections:
An early dinner routine can facilitate quality family time and social connections. By finishing dinner earlier, there is more time for engaging in activities, bonding with loved ones, and participating in community events, ultimately enhancing overall well-being and satisfaction.
Adopting an early dinner routine can yield a multitude of benefits for digestion, sleep quality, weight management, nutrient absorption, hormonal balance, and psychological well-being. By prioritizing an early dinner, you align your eating habits with your body’s natural rhythms, promoting optimal health and vitality. However, it’s important to note that individual preferences and schedules may vary, and the key is to find a mealtime routine that works best for your unique needs. Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the most suitable eating schedule for your personal health goals. Remember, nourishing your body with balanced and timely meals is a powerful step towards achieving overall well-being.
(Disclaimer: The information given here is based on home remedies and general information. Before adopting it, definitely take medical advice. THE MONK does not confirm this.)