Vitamin B7, also known as biotin or vitamin H, is an essential water-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. It is involved in metabolism, cell growth, and the synthesis of fatty acids and amino acids. Its deficiency is relatively rare but can occur due to certain factors, leading to various symptoms and health issues. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and potential consequences of vitamin B7 deficiency.

Causes of Biotin Deficiency
Its deficiency can arise from several factors, including:
Inadequate Dietary Intake
Although biotin is found in many foods, its deficiency can occur if the diet lacks a variety of biotin-rich sources. Foods rich in vitamin B7 include organ meats (liver and kidney), eggs, dairy products, nuts and seeds (especially almonds and peanuts), legumes, whole grains, and certain vegetables (such as sweet potatoes and spinach). Moreover, consuming a highly processed diet with limited sources may contribute to deficiency.
Prolonged Antibiotic Use
Long-term use of antibiotics, particularly broad-spectrum antibiotics, can disrupt the natural gut flora. Bacteria in the gut produce biotin, and the use of antibiotics can reduce their ability to synthesize and release it. This can lead to decreased biotin availability and potential deficiency.
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Certain gastrointestinal disorders can impair biotin absorption or utilization. Conditions like inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, and leaky gut syndrome may affect the absorption of nutrients, including biotin, leading to deficiency.
Genetic Disorders
Some individuals may have genetic disorders that affect the transport and utilization of biotin. One such disorder is biotinidase deficiency, a rare inherited condition where the body is unable to recycle and reuse it effectively. Moreover, this condition requires medical intervention and lifelong biotin supplementation.
Alcoholism
Excessive alcohol consumption can interfere with its absorption and utilization. Alcohol can impair the liver’s ability to store and release biotin, leading to lower levels of biotin in the body. Alcoholics may also have poor dietary habits, further contributing to it deficiency.
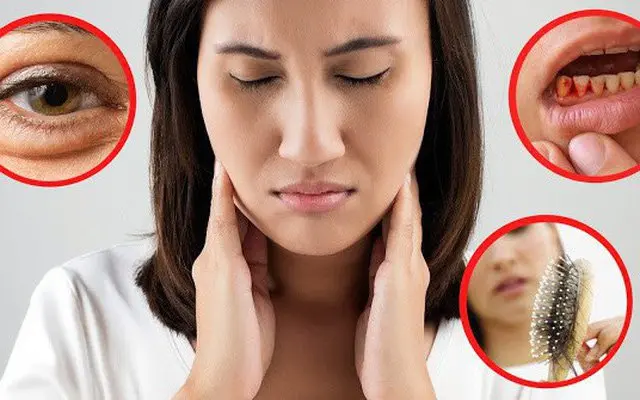
Symptoms of Biotin Deficiency
The symptoms of biotin deficiency can vary and may include:
- Hair and Nail Changes:
One of the hallmark signs of biotin deficiency is hair loss or thinning, as well as brittle, weak nails that may develop ridges or become easily breakable. - Skin Issues:
Its deficiency can manifest as various skin problems, including dry skin, dermatitis (inflammation of the skin), eczema-like rashes, and fungal infections. - Neurological Symptoms:
It plays a role in the normal functioning of the nervous system. Deficiency may lead to neurological symptoms such as depression, fatigue, lethargy, mood changes, numbness or tingling in the extremities, and muscle pain or cramps. - Conjunctivitis:
Its deficiency can cause redness, inflammation, and dryness of the eyes, resulting in conjunctivitis-like symptoms. - Developmental Issues (in Infants):
Severe deficiency in infants can lead to developmental delays, poor muscle tone, and impaired growth.

Consequences of Biotin Deficiency
If left untreated, biotin deficiency can have more severe consequences on overall health and well-being. Some potential complications include:
- Impaired Nutrient Metabolism:
It is involved in numerous metabolic processes, including the breakdown and utilization of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Deficiency can disrupt these processes and impair overall nutrient metabolism. - Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases:
Its deficiency has been associated with an increased risk of developing chronic diseases, including diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and certain types of cancers. However, further research is needed to fully understand the underlying mechanisms. - Pregnancy Complications:
During pregnancy, it plays a vital role in fetal development. Deficiency during pregnancy can increase the risk of birth defects and complications, including malformations of the central nervous system. - Impaired Immune Function:
It is necessary for proper immune system function. Deficiency can also compromise immune responses, making individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
Treatment and Prevention of Biotin Deficiency
Biotin deficiency can be addressed through appropriate treatment and prevention strategies, including:
- Biotin Supplementation:
In cases of severe deficiency or underlying medical conditions, healthcare professionals may recommend biotin supplements. These supplements are available over-the-counter and in prescription strength, depending on the severity of the deficiency. - Dietary Modifications:
Ensuring a balanced diet that includes foods rich in it can help prevent deficiency. Incorporate biotin-rich foods such as eggs, organ meats, nuts and seeds, dairy products, legumes, whole grains, and certain vegetables into your meals. - Addressing Underlying Medical Conditions:
If biotin deficiency is caused by an underlying gastrointestinal disorder or other medical condition, appropriate treatment of the underlying condition is also essential for restoring its levels. - Limiting Alcohol Consumption:
Reducing or eliminating alcohol consumption can help prevent its deficiency and its associated complications. - Probiotics and Gut Health:
Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome through the consumption of probiotics or fermented foods can support the production of B7 by gut bacteria. This can also enhance its availability and absorption.
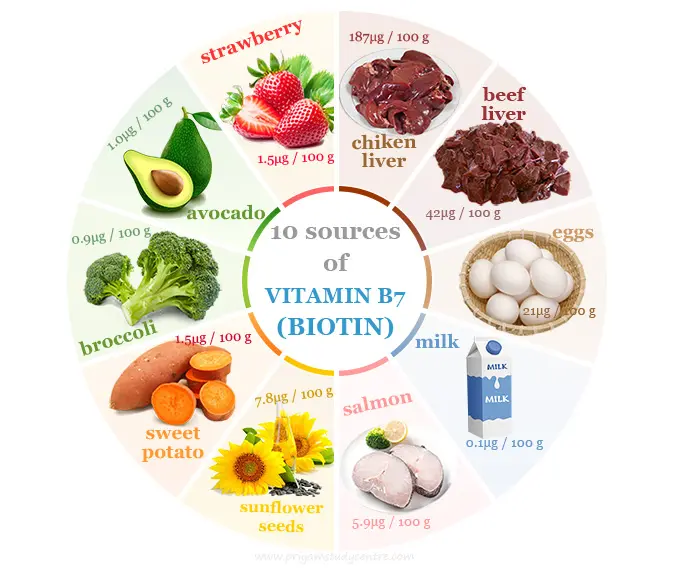
Vitamin B7, is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. Its deficiency can occur due to inadequate dietary intake, certain medical conditions, genetic disorders, or excessive alcohol consumption. Moreover, the symptoms of its deficiency include hair and nail changes, skin problems, neurological symptoms, and developmental issues in infants. Untreated deficiency can also lead to impaired nutrient metabolism, increased risk of chronic diseases, pregnancy complications, and compromised immune function. Also its treatment and prevention strategies involve its supplementation, dietary modifications, addressing underlying medical conditions, and adopting a healthy lifestyle. In addition, if you suspect its deficiency, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and guidance on appropriate treatment options.