When was General Post Office established?
The General Post Office (GPO) in India is the central post office of the country. It was established during the British Raj in 1854. The history of the GPO dates back to the early days of British rule in India, when the East India Company began to establish postal services to facilitate communication and trade.
Before the establishment of the GPO, postal services in India were provided by a network of independent couriers and messengers. They transported letters and parcels between different cities and towns. However, these services were unreliable, inefficient, and expensive, and there was no uniformity in terms of rates and regulations.
In 1837, the East India Company took over the existing postal system. Also, it introduced a uniform rate of postage for all letters and parcels. The first post office in India was established in Calcutta in 1837. Over the next few years, post offices were set up in other major cities and towns.

Need of the post office
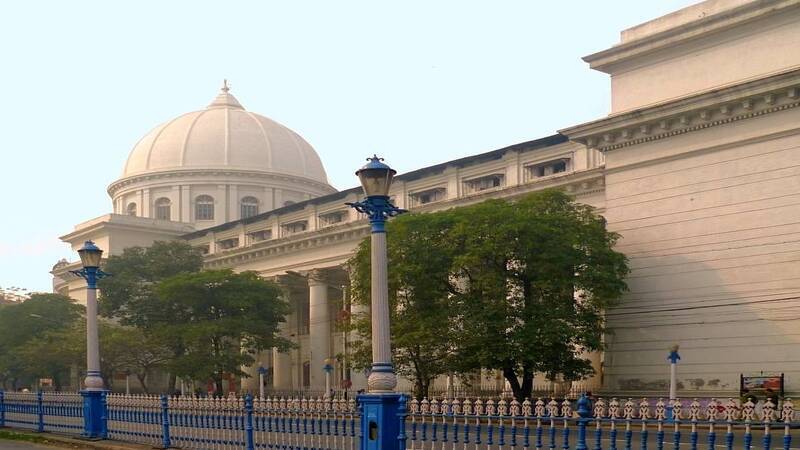
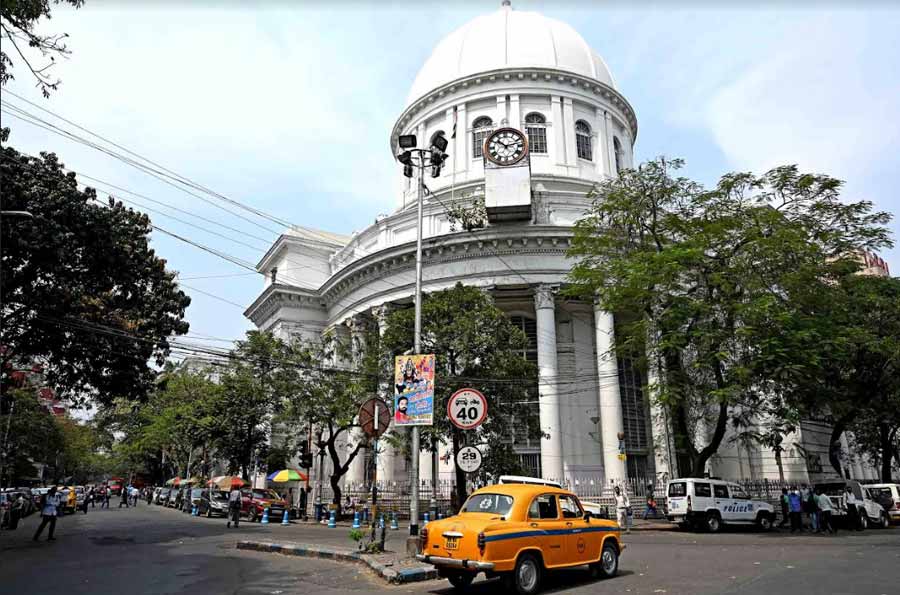
The need for a central post office was felt in the mid-19th century. It was felt because the volume of mail increased and the existing postal network became more complex. In 1854, the GPO was established in Calcutta as the central hub of the Indian postal system. The building was designed by Walter B. Grenville, an engineer in the Public Works Department, and was completed in 1868.
The GPO building in Calcutta was an impressive structure, with a dome that was 220 feet high and a clock tower that was 70 feet high. It was built using white Agra sandstone, and its architecture was inspired by the Italian Renaissance style. The building was equipped with modern amenities, such as gas lighting and a pneumatic tube system. It transported letters and parcels between different floors.
Role of GPO
The GPO played a significant role in the development of the Indian postal system. It served as the headquarters of the Postmaster General of India and provided administrative support to the various post offices across the country. The GPO also introduced several new services, such as money orders, postal orders, and telegraph services. It helped to further streamline the postal network.
Over the years, the GPO has played a crucial role in the history of India. It served as a central hub for communication and trade. During the Indian independence movement, the GPO played a pivotal role in disseminating information and news. It was often a target of attacks by protestors.
Today, the GPO in Calcutta continues to function as the central post office of the country, and is one of the most iconic landmarks of the city. While the volume of mail has decreased with the advent of electronic communication, the GPO remains an important institution, providing a range of services such as philately, postal savings schemes, and retail services. The GPO has also embraced technology, with several initiatives such as e-post, e-money order, and electronic mail tracking, which have helped to modernize the postal system.
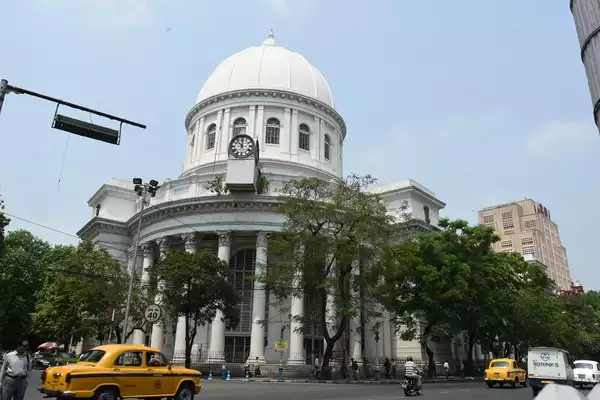

In conclusion, the establishment of the GPO in India marked a significant milestone in the history of the Indian postal system. It helped to streamline the existing postal network, introduced several new services, and played a pivotal role in the development of the country. The GPO remains an iconic landmark of the city of Calcutta. Also, it continues to serve as the central post office of the country, providing a range of services to millions of people across India.