A healthy gut is essential for overall well-being, as it not only facilitates digestion but also influences various aspects of our health, including immunity, mental well-being, and disease prevention. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the strategies and lifestyle choices that can promote gut health and ensure optimal digestive wellness.
Understanding the Gut Microbiota
The gut microbiota refers to the trillions of microorganisms residing in our gastrointestinal tract. Understanding its composition and function is fundamental to maintaining gut health.
The Gut Microbiota: An Introduction
The gut microbiota consists of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms that coexist in a delicate balance. This diverse community performs vital functions, such as aiding digestion, synthesizing essential nutrients, and supporting immune system regulation.
Role of Gut Microbiota in Digestion and Health
The gut microbiota plays a crucial role in breaking down dietary fibers, producing beneficial compounds, and preventing harmful bacteria from flourishing. Additionally, it influences nutrient absorption, immune function, and even mental health.

Factors Affecting Gut Microbiota Composition
Several factors, including diet, lifestyle, medication use, and stress, can impact the composition of the gut microbiota. Understanding these factors helps in making informed choices to maintain a healthy balance.
Diet and Gut Health
A balanced diet forms the foundation of gut health. Certain dietary choices can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria while discouraging the proliferation of harmful ones.
Importance of a Balanced Diet
Consuming a variety of whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, provides the necessary nutrients for a thriving gut microbiota.
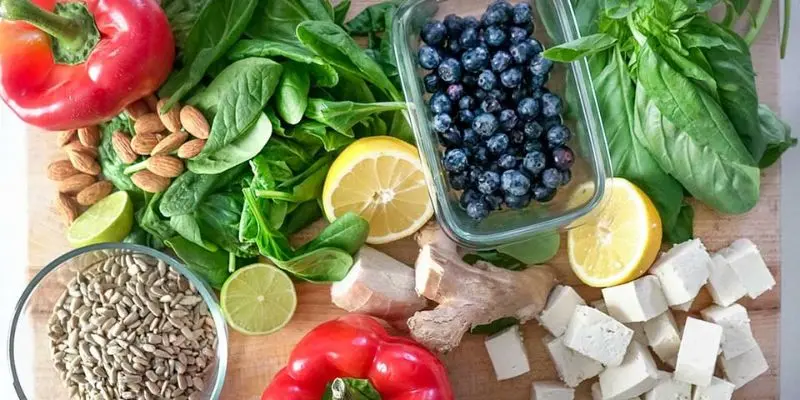

Fiber-Rich Foods: The Foundation of a Healthy Gut
Dietary fiber acts as a prebiotic, nourishing beneficial gut bacteria. Incorporating high-fiber foods like fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains supports regular bowel movements and fosters a diverse microbial community.
Prebiotics and Probiotics: Nourishing the Gut Microbiota
Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria. They can be found in foods like onions, garlic, bananas, and asparagus. Probiotics, on the other hand, are live bacteria or yeasts that confer health benefits when consumed. Sources include yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi.
Fermented Foods: Natural Probiotic Sources
Incorporating fermented foods into the diet provides a natural source of probiotics. These include yogurt, kefir, kombucha, tempeh, and miso. They enhance gut health by introducing beneficial microorganisms.
Avoidance of Artificial Sweeteners and Processed Foods
Artificial sweeteners and heavily processed foods may disrupt the gut microbiota and contribute to gut inflammation. Opting for whole, unprocessed foods and natural sweeteners is more beneficial.
The Role of Healthy Fats
Including sources of healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, in the diet supports the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and contributes to a healthy gut environment.

Lifestyle Choices for a Healthy Gut
In addition to diet, certain lifestyle choices can significantly impact gut health and promote optimal digestion.
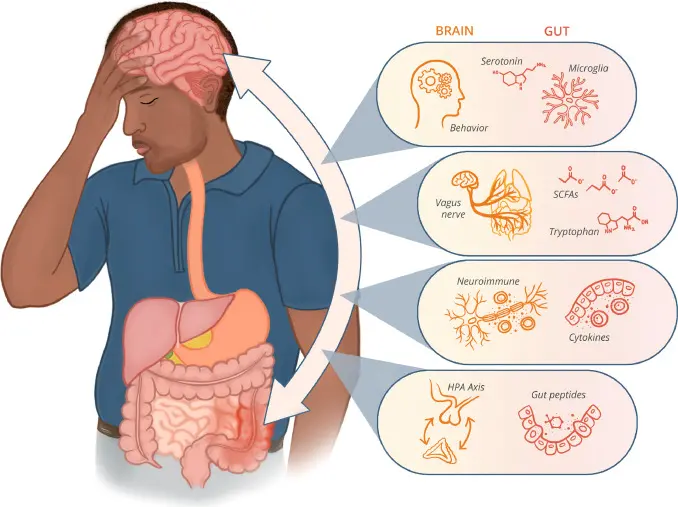
Stress Management: The Gut-Brain Connection
Chronic stress can disrupt the gut microbiota and impair digestion. Engaging in stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, exercise, and adequate sleep supports a healthy gut-brain axis.
Physical Activity and Gut Health
Regular exercise promotes healthy digestion by stimulating intestinal contractions and improving blood flow to the digestive organs. Aim for moderate-intensity activities like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
Adequate Hydration and its Impact on Digestion
Proper hydration is essential for optimal digestion. Drinking an adequate amount of water supports bowel regularity and prevents constipation.
The Importance of Quality Sleep
Insufficient or poor-quality sleep can disrupt the gut microbiota and impair digestion. Establishing a regular sleep routine and creating a sleep-friendly environment promotes gut health.
Avoidance of Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have detrimental effects on gut health. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake can protect the gut and reduce the risk of digestive disorders.

Optimizing Digestion and Gut Health
In addition to dietary and lifestyle choices, certain habits and practices can optimize digestion and support overall intestinal health.
Mindful Eating: Promoting Proper Digestion
Eating slowly, chewing food thoroughly, and savoring each bite aids digestion and nutrient absorption. Practicing mindful eating also promotes a healthy relationship with food.
Chewing and Digestive Enzymes
Chewing food adequately initiates the digestion process. Additionally, certain individuals may benefit from digestive enzyme supplements to support the breakdown of specific nutrients.
Food Combining for Better Digestion
Combining foods strategically can enhance digestion and minimize digestive discomfort. For example, pairing proteins with non-starchy vegetables and avoiding simultaneous consumption of proteins and high-starch foods.
Hygienic Food Preparation and Storage
Practicing proper food hygiene, including thorough washing of fruits and vegetables, safe food storage, and cooking foods to the appropriate temperature, prevents the ingestion of harmful bacteria and protects gut health.
Additional Considerations
Certain circumstances require specific attention to maintain gut health. These include antibiotic use, chronic medication use, allergies, and gastrointestinal disorders.
Antibiotics and their Impact on Gut Microbiota
Antibiotics can disrupt the gut microbiota by killing both harmful and beneficial bacteria. When necessary, it is essential to take probiotics during and after antibiotic treatment to help restore microbial balance.
Chronic Medication and Digestive Wellness
Some medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), can affect health of your gut. Consulting a healthcare professional about potential alternatives or measures to mitigate their impact is advisable.
Gut Health and Allergies
Food allergies and intolerances can trigger gut inflammation and digestive symptoms. Identifying and eliminating trigger foods can improve health of gut in individuals with allergies or sensitivities.
Gastrointestinal Disorders and Gut Health
Individuals with gastrointestinal disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s disease, or ulcerative colitis, require tailored approaches to support gut health. Working closely with healthcare providers and registered dietitians specializing in digestive health is essential.
Maintaining Gut Health in Specific Groups
Different life stages and circumstances require specific considerations to support gut health effectively.
Gut Health for Children and Adolescents
Nurturing a healthy gut microbiota in childhood sets the stage for lifelong gut health. Encouraging a diverse diet, limiting processed foods, and avoiding unnecessary antibiotic use are vital for children and adolescents.
Gut Health during Pregnancy and Postpartum
Pregnancy and the postpartum period significantly impact gut health. Consuming a balanced diet rich in fiber, prebiotics, and probiotics, along with prenatal supplementation, supports the health of both the mother and the developing baby.
Gut Health for the Elderly
Aging can affect gut health due to factors such as reduced digestive function and changes in dietary patterns. Incorporating nutrient-dense foods, regular physical activity, and regular hydration supports health of gut in the elderly population.
Gut Health and Chronic Illnesses
Chronic illnesses like diabetes, obesity, and autoimmune disorders can impact gut health. Managing these conditions through a combination of medication, dietary modifications, and lifestyle adjustments is crucial for maintaining gut health.
Seeking Professional Help
While implementing lifestyle and dietary changes is beneficial, it is essential to seek professional guidance when necessary.
Recognizing the Signs of Gut Imbalance or Dysfunction
Persistent digestive symptoms like bloating, gas, diarrhea, constipation, or abdominal pain may indicate an imbalance or dysfunction in the gut. Recognizing these signs and seeking appropriate care is essential.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional or Registered Dietitian
When experiencing persistent gut-related issues or seeking personalized guidance, consulting a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian specializing in gut health can provide individualized recommendations and support.
Diagnostic Tests for Assessing Gut Health
In some cases, diagnostic tests, such as stool analysis or breath tests, may be recommended to assess gut health and identify specific imbalances or conditions. These tests can help guide targeted interventions for optimal gut health.
Maintaining a healthy gut is vital for overall well-being. By understanding the gut microbiota, making informed dietary choices, adopting a gut-friendly lifestyle, optimizing digestion, and seeking professional help when necessary, individuals can take proactive steps to promote and sustain optimal gut health and digestive wellness. Prioritizing gut health leads to numerous benefits, including improved digestion, enhanced immunity, and better overall health and vitality.
(Disclaimer: This article is for general information only. It cannot in any way be a claim or a substitute for treatment. Always contact your doctor for more details. THE MONK does not confirm this.)