Maternal mental health is a vital component of overall well-being, as it directly influences the emotional, psychological, and social health of both mothers and their families. Pregnancy and the postpartum period can be transformative and joyful, but they can also bring challenges and emotional strain. Additionally, we will discuss strategies for promoting maternal mental health and the importance of seeking support and professional care when needed. By prioritizing maternal mental health, we can create a supportive environment that nurtures the well-being of mothers and fosters healthy and thriving families.
In this article, we will explore the importance of maternal mental health, common mental health disorders experienced during pregnancy and postpartum, risk factors, and the impact on the well-being of mothers and their children
Understanding Maternal Mental Health
a) Emotional Changes in Pregnancy: Pregnancy is a time of significant emotional changes, influenced by hormonal fluctuations, physical adjustments, and anticipation of motherhood. Common emotional experiences include mood swings, anxiety, and occasional feelings of overwhelm.
b) Postpartum Period: The postpartum period, often referred to as the “fourth trimester,” can be accompanied by a range of emotions, including joy, exhaustion, and vulnerability. However, for some mothers, it can also bring about mental health challenges such as postpartum depression, anxiety, or postpartum psychosis.

Common Maternal Mental Health Disorders
a) Postpartum Depression (PPD): PPD is a prevalent mental health disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, guilt, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in activities. It can significantly impact the mother’s ability to care for herself and her child.
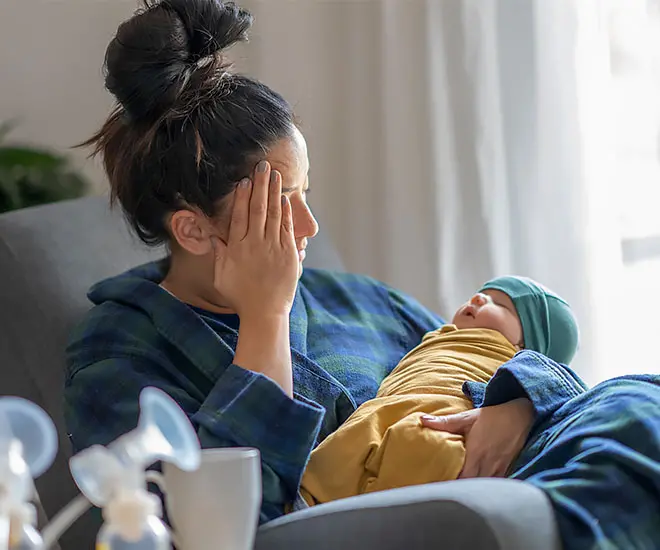

b) Postpartum Anxiety: Postpartum anxiety involves excessive worrying, restlessness, irritability, and physical symptoms such as racing heartbeat and difficulty sleeping. It can interfere with daily functioning and create feelings of distress.
c) Postpartum Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Some women may experience PTSD following a traumatic childbirth experience. Symptoms include flashbacks, intrusive thoughts, hypervigilance, and avoidance of reminders of the trauma.
d) Postpartum Psychosis: Although rare, postpartum psychosis is a severe mental health condition that requires immediate medical attention. It involves hallucinations, delusions, disorganized behavior, and can pose risks to the mother and baby’s safety.
Risk Factors and Impact on Maternal and Child Well-being
a) Biological and Hormonal Factors: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy and postpartum can contribute to mood changes and vulnerability to mental health disorders. Women with a history of mental health conditions are also at a higher risk.
b) Psychosocial Factors: Factors such as a lack of social support, financial stress, relationship difficulties, and a history of trauma can increase the risk of maternal mental health disorders. Cultural factors and stigma surrounding mental health can also impact help-seeking behaviors.
c) Impact on Mothers: Maternal mental health disorders can have far-reaching effects on mothers, affecting their ability to bond with their child, engage in self-care, and maintain overall well-being. It can strain relationships, impact work productivity, and lead to a sense of isolation and guilt.
d) Impact on Children: Maternal mental health directly influences the child’s emotional and cognitive development. Exposure to maternal mental health disorders may increase the risk of developmental delays, behavior problems, and later mental health issues in the child.
Promoting Maternal Mental Health
a) Prenatal Care: Comprehensive prenatal care, including mental health screenings, provides an opportunity to identify and address potential mental health concerns early on. Education about emotional changes and available support resources is crucial.
b) Social Support: Building a strong support network, including family, friends, and community resources, can help mothers feel less isolated and overwhelmed. Peer support groups and online communities can also provide a sense of connection and validation.

c) Self-Care Practices: Encouraging self-care practices, such as getting adequate rest, engaging in physical activity, maintaining a healthy diet, and participating in activities that bring joy and relaxation, can support maternal mental well-being.
d) Open Communication: Encouraging open communication about emotions and mental health within families and communities reduces stigma and creates safe spaces for mothers to express their feelings and seek support.
e) Professional Help: Recognizing the signs of maternal mental health disorders and seeking professional help when needed is crucial. Mental health professionals can provide therapeutic interventions, counseling, and medication if necessary.
Maternal health is important
Maternal mental health is a vital aspect of overall well-being for mothers and their families. Pregnancy and the postpartum period bring significant emotional changes, and it is important to acknowledge and address the potential challenges that can arise during this time. By understanding the common mental health disorders experienced by mothers, the risk factors involved, and the impact on maternal and child well-being, we can take proactive steps to support and promote maternal mental health. Cultivating a supportive environment that encourages open communication, access to resources, and destigmatization of mental health concerns is essential. By prioritizing maternal mental health, we empower mothers to seek help, create healthy and nurturing environments for their children, and contribute to the well-being of families and communities as a whole. Together, we can ensure that mothers receive the care, support, and understanding they need to thrive during the transformative journey of motherhood.
(Disclaimer: The information given here is based on general information. Before adopting it, definitely take medical advice. THE MONK does not confirm this.)